Concussion Basics (General Information)
Key Points:
A concussion is a temporary disturbance of brain function.
There are a variety of symptoms you may feel with a concussion
You can expect to fully recover but timelines vary for each person.
See your doctor or go to the emergency department to confirm if you have had a concussion.
What is a Concussion?
A concussion is caused by a bump, blow, or jolt to the head, or by a hit to the body that causes the head and brain to move rapidly back and forth in the skull. This can create a temporary disruption of the brain’s function.
A concussion is also called a mild traumatic brain injury—or mTBI. It is important to remember that the brain can repair these “disruptions."
"What is happening to my brain?"
Your brain floats in a bath of fluid inside your skull. A strong impact to your head makes the brain swish back and forth inside your skull creating strain on the brain cells that make up the substance of your brain.
Stretching of the neurons📝Cells that use electrical signals to carry messages around your body. temporarily disrupts their function. It’s as if your phone’s charging cord is a bit worn out so that it takes longer to charge the battery. The cord is still working, but not as well.
Causes of Concussions
Concussion in adolescents can occur from a fall, a car accident, or during sports. Certain sports such as hockey, soccer, mountain biking, skiing, motorsports, and gymnastics have a higher risk of concussions.
How do you know if you had a concussion?
Sometimes it can be hard to know if you suffered a concussion. For example, you may not feel unwell or symptomatic until after your soccer game is over. Other times, you may feel a headache or not feel “right” immediately.

The key message is: if you are not sure – act as if it is a concussion. Remove yourself from the game or situation, and let an adult know. You should get follow up with your doctor to determine if you have had a concussion.
What does a concussion feel like?
There are a list of common symptoms affecting how your body feels, how you think, your emotions, and how you socialize with others. Everyone has a slightly different experience, but most people will have some, or all of the symptoms in the symptom wheel. Sometimes your symptoms feel a little worse the next day. Just like a sprained ankle that is more swollen the next day, the brain cells respond to injury slowly.
Are any of these symptoms familiar to you?
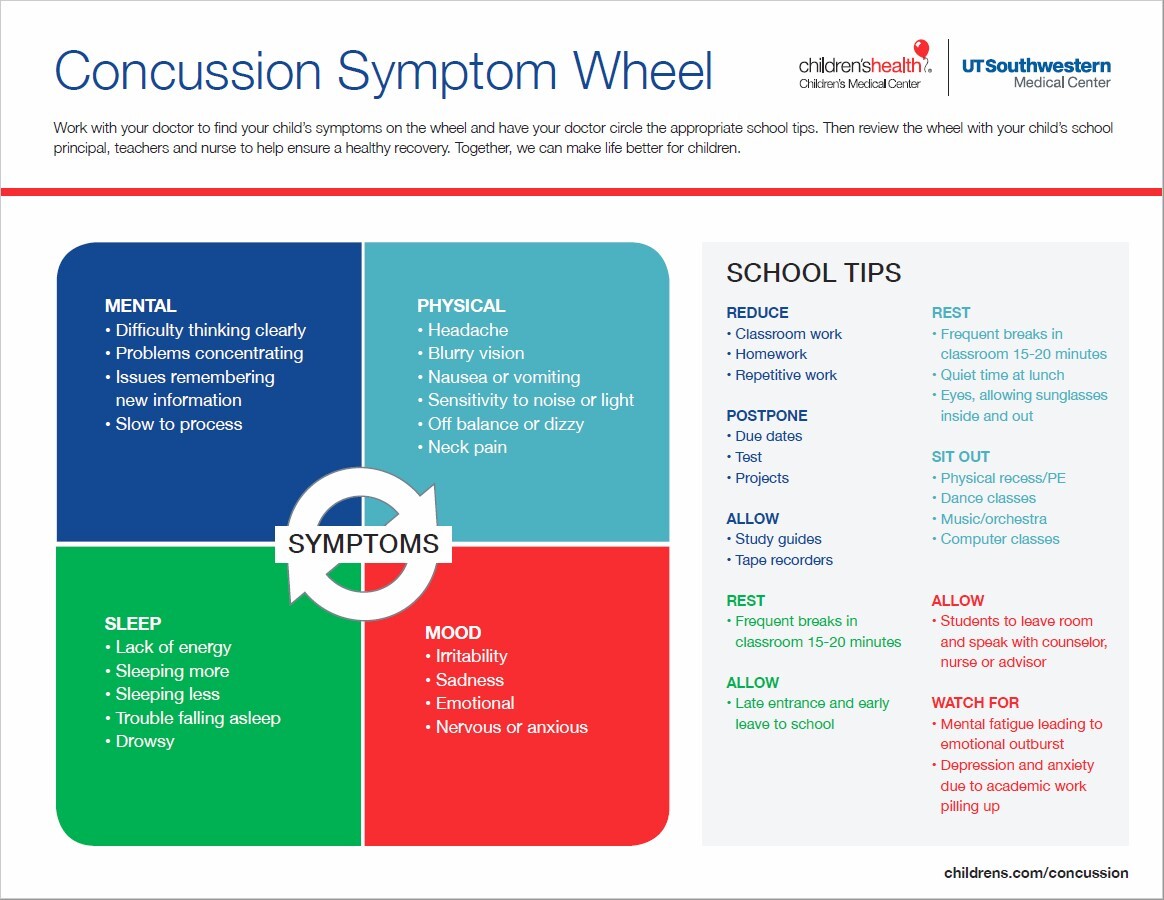
Some people find that they are more prone to hit their head after having a concussion. Not every hit or contact with your head results in a concussion. Hitting a door or cupboard may cause pain and external injury, but not an injury to your brain.
On the other hand, it is important to recognize the signs of a medical emergency due to a hit to your head. If you experience any of the following:
You lose consciousness or have a deteriorating conscious state.
You experience the most severe headache of your life.
You experience weakness or tingling/burning in arms or legs.
You experience slurred speech, vomiting, or double vision.
You experience seizure📝A burst of uncontrolled electrical activity between brain cells, which can cause temporary changes in muscle or movements (stiffness, twitches, or limpness) behaviours, sensations or states of awareness. (https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/epilepsy/types-of-seizures)s or convulsion.
In these cases do not hesitate and get to an emergency department right away.